The eletrocardiograma, or ECG, measures the heart’s electrical activity. While most athletes are healthy, screening is vital because some heart conditions stay silent until the body reaches maximum effort. A normal resting pulse may hide conduction issues or structural abnormalities that appear only during intense exercise. The goal of athlete ECG screening is early detection. By identifying irregularities early, sports professionals can train smarter, prevent long term damage and protect performance longevity.
Why Athletes Need ECG Screening
Sports place unique demands on the heart. Long distance runners develop high cardiac output. Weight lifters push sudden pressure spikes. Football and basketball players switch between rest and near sprint pace within seconds. This spectrum of physical stress influences electrical rhythm and sometimes reveals hidden vulnerabilities. Eletrocardiograma for Athletes is used widely across competitive sports programs because it gives doctors a clear picture of how the heart behaves during training cycles.
Some conditions that ECG may detect early include arrhythmias, prolonged intervals, conduction block, early repolarization abnormalities and hypertrophic changes. These findings do not always mean an athlete must stop training. In many cases, they simply require monitoring or lifestyle adjustment. The key advantage is knowledge. When athletes know how their heart responds to activity, they can build training with confidence instead of risk.
What ECG Measures in Athletes
ECG maps electrical impulses as they travel across the heart muscle. The tracing shows the speed and sequence of every beat. In athletes, several natural adaptations appear on the ECG. These include slower resting heart rate, increased vagal tone and sometimes mild bradycardia. These findings are normal in trained individuals. However, some ECG variations require further evaluation, especially when they suggest abnormal conduction or stress response.
Eletrocardiograma for Athletes helps distinguish normal athletic changes from patterns that require caution. For example, early repolarization can be normal, but ST segment changes may indicate risk. Likewise, sinus bradycardia may reflect conditioning, while irregular pauses may require medical review. Doctors trained in sports cardiology evaluate these patterns with experience and context.
How ECG Screening Works for Athletes
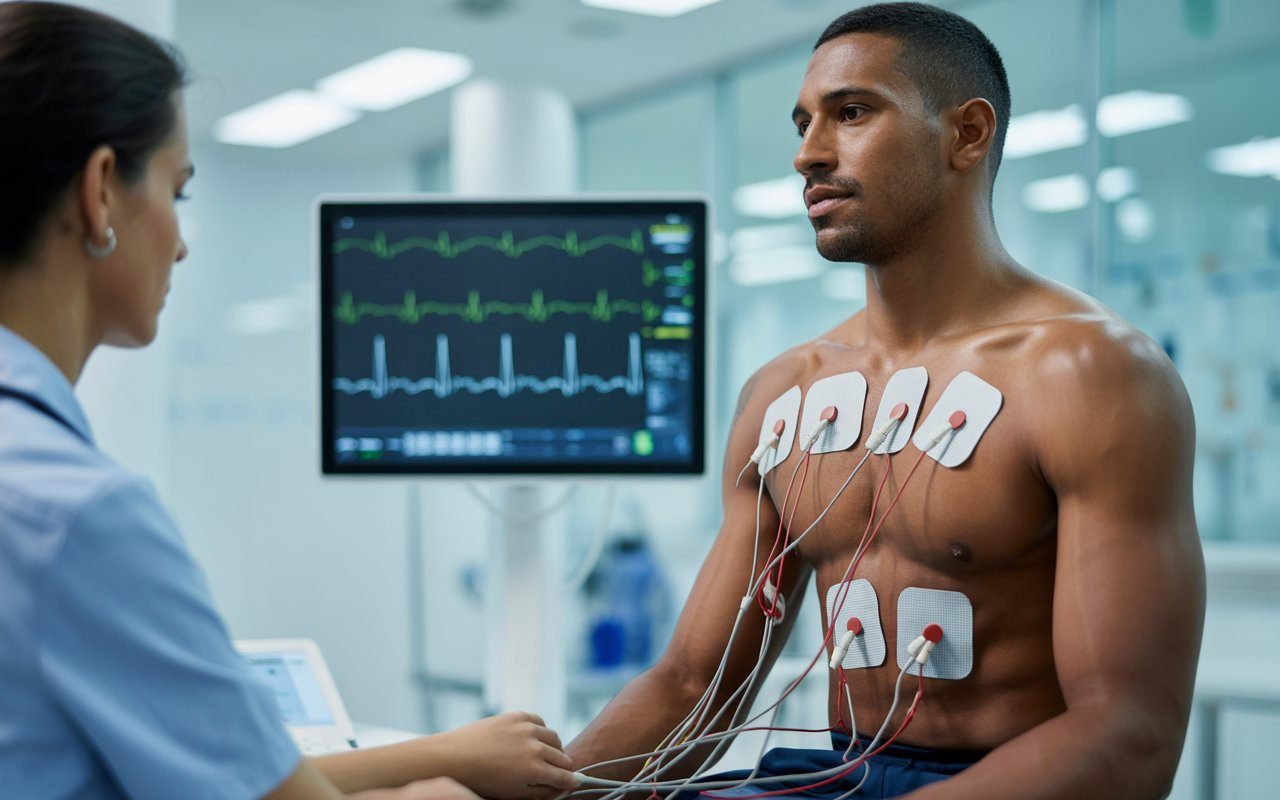
ECG screening for sports is similar to a standard clinical ECG, but the interpretation differs. Athletic hearts behave differently from sedentary hearts. The test begins with the athlete sitting or lying relaxed as electrodes are placed on the chest and sometimes on the limbs. These sensors detect electrical activity without sending energy into the body. The recording lasts only a few seconds. Afterward, the doctor studies the printed curve for rhythm intervals, heartbeat shape and wave progression.
A full demonstration of ECG placement can be viewed in the step by step guide. This resource shows electrode positioning and testing workflow clearly. Many athletes find it reassuring to see how simple the procedure is before their first screening.
When Athletes Should Get an ECG
Routine ECG screening is recommended for athletes starting high intensity sports, participating in organized competitions or training more than five days per week. Screening is also helpful when symptoms appear during or after exercise. Palpitations, chest tightness, breathlessness out of proportion to effort or dizziness during activity are signs that the heart may need a closer look.
A useful reference for personal risk evaluation is the guide on who should ECG, which explains common categories where testing is recommended. Young athletes with family history of arrhythmias or sudden cardiac conditions should be especially protected with ECG monitoring.
Benefits of ECG for Sports Performance
Eletrocardiograma for Athletes is not only about safety. It also improves athletic performance through knowledge. When athletes train incorrectly, fatigue increases and progression slows. When heart rhythm responds positively to training, endurance grows predictably. ECG helps coaches adjust training intensity based on how the athlete’s cardiovascular system handles stress. Balanced training reduces injury risk and improves recovery time.
ECG screening also empowers athletes mentally. Many competitors perform better when they know that their body is functioning safely. Confidence is a powerful tool. Athletes with confirmed healthy rhythm push cleanly without hesitation. Those with early findings can adjust before symptoms appear.
ECG vs Stress ECG for Athletes
Resting ECG gives information at baseline, but many athletic arrhythmias appear only under physical stress. For this reason, some programs use a stress based version of the exam. Stress ECG involves recording the heart rhythm while the athlete exercises at increasing intensity. The goal is to simulate game conditions inside the clinic. This expanded method is discussed in detail in the stress exercise article.
Both resting and stress ECG have value. Rest ECG is fast, accessible and often enough for early assessment. Stress ECG reveals exercise specific patterns. Combining both gives the clearest overall picture of athletic heart function.
Global Sports Medicine Perspective (External)
Sports cardiology specialists highlight ECG as a key screening tool for athletes because it detects electrical abnormalities linked to sudden cardiac events. One medical resource describes ECG screening as essential in reducing risk during competitive sports participation and encourages athletes with symptoms to undergo formal evaluation. You can read clinical discussion on athlete ECG safety at athlete ECG.
Research published in a sports cardiology review emphasizes the role of ECG in detecting silent arrhythmia, conduction disease and repolarization variants in athletes. The authors conclude that ECG can be useful for risk reduction when interpreted with athletic physiology in mind. The review can be viewed at sports ECG.
Risk and Limitation Considerations
ECG is a safe tool for athletes, but it is not a complete diagnosis alone. It shows electrical activity but cannot evaluate heart structure or blood flow. When ECG suggests abnormalities, doctors may request echocardiogram, Holter monitoring or exercise imaging studies. These additional tests give deeper clarity when required. The purpose of ECG is not to label athletes unnecessarily, but to create a strong foundation for heart protected training.
ECG for Professional vs Amateur Athletes
Professional athletes often complete regular ECG assessments throughout the season. Amateurs may only need screening when symptoms appear or when training intensity increases. Young athletes in school sports sometimes receive ECG before tournaments or when heart history exists in the family. The goal in all levels is the same. Protect health and encourage longevity in sport.
Final Summary
Eletrocardiograma for Athletes is a reliable way to understand heart performance in sport. It is fast, painless and extremely helpful for early detection. When results are normal, athletes gain confidence and train at full power. When findings appear, early management prevents complications. ECG is not only a safety tool, but a performance strategy. A strong athlete trains with precision. A protected athlete competes with trust.